MCQs on Purine metabolism:
1. The function of nucleotide includes:
A. Second Messenger
B. Energy currency and high energy equivalents
C. Regulators of intermediary metabolism
D. All of the above
Answer: D
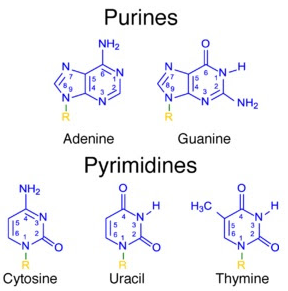
2. Purines and Pyrimidines are the nitrogen bases present on the nucleotides.
Which of the following is a purine base?
A. Adenosine
B. Cytosine
C. Thymine
D. Uracil
Answer: A
3. Nucleotides are:
A. Purine bases
B. Nitrogen bases+ Pentose Sugar
C. Nitrogen bases + Pentose sugar + Phosphate
D. None of the above
Answer: C
4. Which of the following is not the precursor for the de novo purine biosynthesis?
A. Aspartic Acid
B. Glycine
C. Glutamine
D. Arginine
Answer: D
5. Which of the following serves as the cofactor for the de novo synthesis of purine metabolism?
A. Thiamine
B. Biotin
C. Folate
D. Flavin
Answer: C
6. What is an activator of the enzyme “Glutamine: Phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate amido transferase” a committed step of de novo biosynthesis of purines?
A. Adenosine Monophosphate
B. Guanosine Monophosphate
C. Inosine Monophosphate
D. Phosphoribosyl Pyrophosphate
Answer: D
7. Which of the following is the correct statement regarding Sulfonamides?
A. Structural analogs of PABA that competitively inhibit bacterial synthesis of folic acid
B. Structural analogs of PABA that competitively inhibit the human synthesis of folic acid
C. Structural analogs of PABA that competitively inhibit the bacterial and human synthesis of folic acid
D. None of the above
Answer: A
8. Trimethoprim is a potent antibacterial compound that selectively inhibits bacterial…………………….
A. Formyl transferase
B. PRPP synthetase
C. Dihydrofolate reductase
D. None of the above
Answer: C
9. Which of the following is the coenzyme for the synthesis of deoxyribonucleotides catalyzed by an enzyme ribonucleotide reductase?
A. Glutathione
B. Thioredoxin
C. NADPH
D. FADH
Answer: B
10. Severe combined immunodeficiency disease is caused by the deficiency in which of the following enzyme?
A. AMP deaminase
B. Adenosine deaminase
C. PRPP synthetase
D. None of the above
Answer: B
MCQ Questions on Pyrimidine Metabolism
11. Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase II (CPS-II) is the committed step in the formation of carbamoyl phosphate is:
A. Activated by PRPP
B. Inhibited by UMP
C. Activated by ATP
D. All of the above
Answer: D
12. Which of the following cofactor is used during the conversion of uracil to thymine?
A. S-Adenosyl Methionine
B. Tetrahydrofolate
C. Tetrahydrobiopterin
D. Biotin
Answer: B
13. Which of the following cofactor/coenzyme is NOT utilized in the conversion of ribose to deoxyribose?
A. NADPH
B. FADH2
C. UMP
D. Thioredoxin
Answer: C
14. Followings are the example of nucleosides, EXCEPT:
A. Adenosine
B. Cytidine
C. Cytosine
D. Uridine
Answer: C
15. The Nitrogen of a purine molecule are derived from all of the following amino acids, except?
A. Aspartic Acid and Glutamine
B. Asparagine and Glutamine
C. Glutamate and Alanine
D. Glycine and Alanine
Answer: A
16. Which of the following steps of pyrimidine biosynthesis occurs in mitochondria?
A. Synthesis of carbamoyl phosphate catalyzed by CPS II
B. Conversion of carbamoyl phosphate to carbamoyl aspartate catalyzed by aspartate trans carbamoylase
C. Synthesis of dihydroorotate catalyzed by dihydroorotase
D. Formation of orotic acid catalyzed by dihydroorotase dehydrogenase
Answer: D
17. Methotrexate inhibits which of the following enzyme?
A. ribonucleotide reductase
B. thymidylate synthase
C. dihydrofolate reductase
D. PRPP‑amido transferase
Answer: B
18. Orotic aciduria is an inherited genetic disorder caused by a deficiency in which of the following enzyme?
A. CPS II
B. Aspartate trans carbamoylase
C. Dihydroorotase dehydrogenase
D. UMP synthase
Answer: D
19. Fluorouracil is an anti-tumor agent that binds and irreversibly inhibits which of the following enzyme?
A. ribonucleotide reductase
B. thymidylate synthase
C. dihydrofolate reductase
D. PRPP‑amido transferase
Answer: B
20. Which of the following is the degradation product of pyrimidines?
A. beta-alanine
B. Uric acid
C. Allantoin
D. Glycine
Answer: A