ELECTRICAL DRIVES & CONTROL LAB VIVA Questions :-
1. What is Switched Reluctance Motor?
The switched reluctance motor is a double salient, singly excited motor. This means that it has salient pole on the rotor and the stator, but only one member carries windings. The rotor has no windings, magnets or cage windings. It works on variable reluctance principle.
2. What are the two types of control techniques in SRM?
- Hysteresis type control
- PWM type control
3. What is meant by energy ratio?
Energy ratio = Wm/Wm + R. = 0.455
Wm = mechanical energy transformed
This energy ratio cannot be called as efficiency. As the stored energy R is not wasted as a loss but it is fed back to the source through feedback diodes.
4. What is phase wingdings?
Stator poles carrying field coils. The field coils of opposite poles are connected in series such that mmfs are additive and they are called phase wingdings of SRM.
5. What are the major difference between SRM and stepper motor?
difference between SRM and stepper motor
6. What is hysteresis current control?
This type of current controller maintains a more or less constant current throughout the conduction period in each phase. This controller is called hysteresis type controller.
7. When do you go for chopping mode of control in switched reluctance motor?
The chopping mode of control in SRM is applied only low-speed. Here each phase winding gets excited for a period which is sufficiently long.
8. What is the working principle of Switching Reluctance Motor?
- The switched reluctance motor basic principle is based on Faraday’s law of electro magnetic interaction.
- Whenever a current carrying conductor is placed in a magnetic field, it experiences a force. The direction of force given by Fleming’s left hand rule.
- SRM is a single excited and double salient pole electric motor. Due to the variation of reluctance the motor should be operated.
- The SRM develops a torque due to variable reluctance.
- When air gap is minimum, the reluctance will be minimum; hence inductance will be maximum.
- So the rate of change of inductance is zero.
- When the reluctance various in the motor, there will be a change in inductance so when a particular stator winding of SRM is energized,the rotor pole comes in alignment with that stator pole and thus the rotor rotates.
9. Why rotor position sensor is essential for the operation of Switched Reluctance Motor?
It is normally necessary to use a rotor position sensor for commutation and speed feed back. The turning ON and OFF operation of the various devices of power semiconductor switching circuit are influenced by signals obtained from rotor position sensor.
10. List the disadvantages of a Switched Reluctance Motor?
- Stator phase winding should be capable of carrying magnetizing current.
- For high-speed operation developed torque has undesirable ripples is a result develops undesirable noises or acoustic noises.
- For high-speed current waveform has undesirable harmonics to suppress this effect large size capacitor is to be connected.
- It requires position sensors.
11. What are the advantages of switched reluctance motor?
- Construction is simple and robust.
- Rotor carries no windings, no slip rings, no brushes, less maintenance.
- There is no permanent magnets.
- Ventilating system is simpler as losses takes place mostly in the stator.
- Power semiconductor switching circuitry is simpler.
- No shoot through fault likely to happen power short circuits.
- Developed torque does not depends upon the polarity of current in the phase winding.
- The operation of the machine can be easily change from motoring mode to generating mode by varying the region of conduction.
- It is possible to get very high-speed.
- Depending upon the requirement T-w characteristics can be achieved.
- It is the self-starting machine.
- Energy stored in the phase winding is fed back to the supply through the feedback diodes during off period.
12. Whar are the applications of SRM?
- Washing machines
- Vacuum cleaners
- Fans
- Future auto mobile applications
- Robotics control applications
13. What is the difference between Synchronous Reluctance Motor and PM Synchronous Motor?
difference between Synchronous Reluctance Motor and PM Synchronous Motor
14. What are the differences between PMBLDC and PMSM?
differences between PMBLDC and PMSM
15. Distinguish between self-control and vector control of PMSM
Difference between self-control and vector control of PMSM
16. What is meant by slotless motor?
In slotless motor, the stator teeth are removed and resulting space is partially filled with addition of copper
17. State the advantages of PMSM?
- Improved performance
- Reliability increases
- Reduced components
- Versatility of the controller
- Less cost
18. What are the advantages and disadvantages of PMSM?
Advantages:
- It runs at constant speed.
- No field winding, no field loss, better efficiency.
- No sliding contacts, so it requires less maintenance.
Disadvantages:
- Power factor of operation can not be controlled as field winding cannot be controlled.
- It leads to losses and decreases efficiency
19. Write the EMF equation of PMSM
Eph = 4.44 f. Fm. Kp. Kb. Nph volts
This is the RMS value of induced EMF per phase
where
f – frequency in Hz
Nph – Turns per phase
Fm – Flux per pole
Kw – Winding factor
20. What are the assumptions made in derivation of EMF equation for PMSM?
Flux density distribution in the air gap is sinusoidal.
Rotor rotates with a uniform angular velocity of ?m(r/sec).
Armature winding consists of full pitched, concentrated similarly located coils of equal number of turns.
21. Why PMSM operating in self-controlled mode is known as Commutatorless DC Motor?
Load side controller performs somewhat similar function as commutator in a DC machine. The load side converter and synchronous motor combination functions similar to a DC machine.
First it is fed from a DC supply and secondly like a DC machine. The stator and rotor field remain stationary with respect to each other at all speeds. Consequently, the drive consisting of load side converter and synchronous motor is known as commutator less DC motor.
22. What is Pulse Mode?
- For speeds below 10% of base speed, the commutation of load side converter SCRs is done by forcing the current through the conducting SCRs to zero.
- This is realised by making source side converter to work as inverter each time load side converter SCRs are to be turned off.
- Since the frequency of operation of load side converter is very low compared to the source frequency, such kind of operation can be realised.
- The operation of inverter is termed as Pulsed Mode.
23. What is Load Commutation?
Commutation of thyristors by induced voltages of load is known as Load Commutation. Here, frequency of operation is higher and it does not require commutation circuits.
24. What is meant by self-control?
- As the rotor speed changes the armature supply frequency is also changes proportionally so that the armature field always moves (rotates) at the same speed as the motor.
- The armature and rotor field move in synchronism for all operating points.
- Here accurate tracking of speed by frequency is realised with the help of rotor position sensor.
ELECTRICAL DRIVES & CONTROL LAB VIVA Questions :-
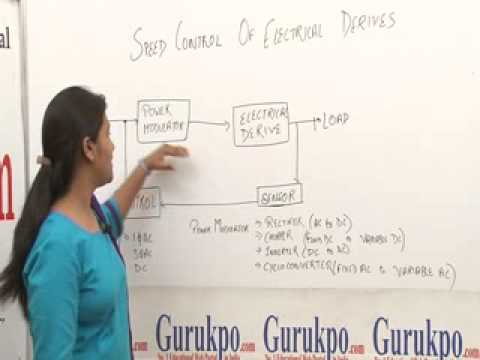
1. What is meant by electrical drive?
2. Draw the block diagram of an electrical drive system.
3. Draw the mechanical characteristics of DC series motor.
4. Define plugging in three phase induction motor.
5. Why a starter is necessary for a DC motor?
6. Name the various types of starters commonly used for starting an induction motor.
7. What is static Ward-Leonard drive?
8. State the advantages of DC chopper drives.
9. Mention some of the merits and demerits of AC drives.
10. What is meant by v/f control?
11. Explain about OLR coil
12. Mention different types of three phase motor starters.
13. Mention the factors affecting the speed of a DC motor.
14. State the advantages of flux control method.
15. List the various advantages of DC Chopper.
16. Bring out the starting current equation and explain how it
Reaches the very high value.
17. What is the need of NVC in starter?
18. Draw the general block diagram of starter circuit.
19. List the various methods of controlling speed of DC shunt
Motor.
20. What do you mean by controlled rectifier?
PART B
1. Explain different types of electric drives and its applications to Industry.
2. What are the different classes of motor duty and explain in detail?
3. What are the different electrical braking methods used in electrical Drives? Explain any one method applied to DC shunt motor.
4. Draw and explain the torque – speed characteristics of three phase induction motor with necessary equation.
5. Describe the principle of starting of DC shunt motor using power and Control circuit with neat circuit diagram.
6. What do you understand by the term soft start? Explain the soft start
Method employed for induction motor?
7. Discuss in brief various conventional methods of speed control of DC motors.
8. Draw and explain some of the commonly used controlled rectifier circuits for DC drive.
9. Explain the method of control of three phase induction motor by
(i) Stator voltage control
(ii) Frequency control
10. Explain with neat sketch the static Kramer variable speed drive system used for slip power recovery.
11. List out the types of starters utilized for three phase squirrel cage induction motor.
12. What type of starter used in three phase slip ring induction motor?
13. What is a controlled rectifier and how the concept is Implemented in DC choppers and mentions its advantages.
14. Explain briefly about typical starting control circuits of DC shunt and Series motors.
15. Explain neatly about the types of speed control methods in DC shunt Motors.
16. Draw and explain neatly about the four types of flux control process in DC series Motor.