SKIN Multiple Choice Questions :-
1. Healthy skin requires special care to maintain its health, elasticity, vibrancy and?
A. color
B. pallor
C. dryness
D. dullness
Answer: A
2. What is the technical name for the study, including its structure, functions and treatment?
A. etiology
B. anatomy
C. pathology
D. dermatology
Answer: D
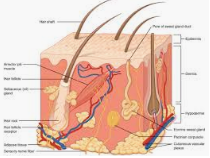
3. The outermost layer of the skin is called the ?
A. corium
B. dermis
C. adipose
D. epidermis
Answer: D
4. Which of the following layers of skin does not contain and blood vessels?
A. cutis
B. dermis
C. corium
D. epidermis
Answer: D
5. What is another name for the stratum germinativum?
A. epidermis
B. dermal layer
C. stratum lucidum
D. basal layer or stratum basale
Answer: D
6. Where does mitosis (cell division) or replacment of the skin take place?
A. stratum lucidum
B. stratum corneum
C. stratum granulosm
D. statum greminativum
Answer: D
7. The stratum germinativm and what other layer of skin contain melanin?
A. dermis
B. subcutaneous
C. stratum corneum
D. stratum spinosum
Answer: D
8. On the human body, the thickest skin is located on the:
A. thighs
B. buttocks
C. abdomen
D. palms and soles
Answer: D
9. The layer of the epidermis that sheds keratin cells that are constantly replaced is the?
A. stratum lucidum
B. stratum corneum
C. stratum mucosum
D. stratum granlosum
Answer: B
10. What quality is notable about the stratum corneum?
A. it is the thinnest layer of skin
B. it is the weakest layer of skin
C. it is the toughest layer of skin
D. it is lowermost layer of skin
Answer: C
11. After hepatitis B vaccination child with allergic family history and pruritis involving face & convexities developed numerous umblicated vesicles; which became pustular & haemorhagic & crusted. After 2 days child developed high fever and lymphadenopathy. The diagnosis is
A. Secondary infected atopic dermatitis
B. Molluscum contagiosum
C. Eczema herpaticum
D. Eczema vaccinatum
Answer: C
12. A 40 year old male reported with recurrent episodes of oral ulcers, large areas of denuded skin and flacid vesiculo-bullous eruptions. Which is the most important bed-side investigation helpful in establishing the diagnosis
A. Gram staining of the blister fluid
B. Culture and sensitivity
C. Skin biopsy and immunoflurescence
D. Tzanck smear from the floor of bulla
Answer: D
13. True about pemphigus vulgaris A/E:
A. Subepidermal
B. Autoimmune disease
C. Tzanck smear shows acanthoyltic cells
D. Antibody are formed against desmogleins
Answer: A
14. A girl about to marry has comedonal acne. Drug to treat such a case is: March 2013
A. Topical antibiotic
B. Benzoyl peroxide
C. Retinoids
D. Estrogen
Answer: C
15. Koebner phenomenon seen in ?
A. Psoriasis
B. Lichen planus
C. Warts
D. All the above
Answer: D
16. Heliotopre sign is seen in ?
A. Dermatomyositis
B. Scleroderma
C. Photodermatitis
D. Vitiligo
Answer: A
17. Patient presents with discharge per urethrum and microscopy shows presence of intracytoplasmic gram negative cocci; what is the most probable diagnosis ?
A. Gonorrhea
B. Donovanosis
C. Bacterial vaginosis
D. Syphilis
Answer: A
18. Christmas tree appearance in skin is seen in ?
A. Pityriasis rosea
B. Pityriasisrubrapilaris
C. Psoriasis
D. Vitiligo
Answer: A
19. Pomphylox affects ?
A. Palms & soles
B. Groin
C. Scalp
D. Trunk
Answer: A
20. Erythrasma is caused by ?
A. Comybacterium
B. Staphylococcus
C. Streptococcus
D. Herpes Virus
Answer: A
21. HPV causes ?
A. Condylomalata
B. Condyloma acuminata
C. Bubo
D. Chancre
Answer: B
22. Drug of choice for genital warts is ?
A. Acyclovir
B. Podophyllin
C. Minocyclin
D. Interferon alpha
Answer: B
23. Depigmenting agent of choice in in treatment of dermatological disorders is
A. Hydroquinone
B. Zinc
C. Kojic acid
D. Azelaic acid
Answer: A
24. Nail pitting is seen with ?
A. Paronychia
B. Ectodermal dysplasia
C. Alopecia areate
D. All the above
Answer: D
25. Vitiligo is associated with the following except
A. Addison’s disease
B. Men syndrome
C. Pernicious anemia
D. Crohns disease
Answer: D
26. True about erythema toxicum neonatorum is ?
A. It is present in 3 – 5 % of the newborns
B. It is mostly present at birth
C. It is called the flea bitten rash of newborn
D. Topical antibiotics is the treatment of choice
Answer: C
27. What is the the most probable diagnosis of a child who presents with white umbilicated lesions on face?
A. Molluscumcontagiosum
B. Herpes simplex infection
C. Erythema toxicum neonatorum
D. Human papilloma virus infection
Answer: A
28. Haascheiben cells in epidermis are responsible for?
A. Touch
B. Temperature
C. Pressure
D. Proprioception
Answer: A
29. Apple jelly noddule is seen in ?
A. Lupus vulgaris
B. Cutaneous anaphylaxus
C. Erythroderma
D. Erysepals
Answer: A
30. Flaccid bullae with mucosal involvement and intraepidermal acantholysis are characteristic of?
A. Pemphygus vulgaris
B. Pemphigus foliaceous
C. Psoriasis
D. Vitiligo
Answer: A
31. Ig A deposition in dermo epidermal junction skin seen in ?
A. Dermatitis herpetiformis
B. Bullous pemphigoid
C. Linear IgA disease
D. Epidermolysis bullosa
Answer: C
32. Not a feature of scabies is ?
A. Serpentine burrow
B. Severe itching
C. Web space affection
D. Genitalia are not affected
Answer: D
33. True about the lesions of lichen planus ?
A. Polygonal violaceous paple
B. Affect skin and mucous membranes
C. Are pruritic
D. All the above
Answer: D
34. Antigen defect in Pemphigus Vulgaris
A. Desmoglein-1
B. Desmoglein-3
C. Desmocollin-3
D. Desmocollin-2
Answer: B
35. Color of tuberous sclerosis lesions on wood lamp examination ?
A. Bright green
B. Milky white
C. Golden yellow
D. Blue white
Answer: D
36. Alopecia areata is a/ an ?
A. Autoimmune disorder
B. Allergic disorder
C. Anaphylactic disorder
D. Bacterial infection
Answer: A
37. Whitfield’s ointment consists of ?
A. 3% salicylic acid + 6% benzoic acid
B. 3% benzoic acid + 6% salicylic acid
C. 2% salicylic acid + 4% benzoic acid
D. 2% benzoic acid + 4% salicylic acid
Answer: A
38. Sphagetti and meat ball appearance is seen in ?
A. Pityriasis rosacae
B. Tinea capitis
C. Tinea carporis
D. Tinea versicolor
Answer: D
39. Which of the following can cause both cicatricial as well as Noncicatricial alopecia ?
A. Alopecia areata
B. Telogen effluvium
C. SLE
D. Hypothyroidism
Answer: C
40. Miliaria arises from obstruction of ?
A. Eccrine sweat glands
B. Apocrine sweat glands
C. Sebaceous glands
D. Ectopic sebaceous glands
Answer: A
41. Patchy hair loss with velvety skin points to the diagnosis of
A. Alopecia aereata
B. Trichotelomania
C. Hyperthyroidism
D. Adenoma sebacicum
Answer: C
42. Black piedra is caused by ?
A. Piedraia hortae
B. Trichosporon asahi
C. Trichosporon ovoides
D. Trichosporon inkin
Answer: A
43. In scabies which skin layer is affected?
A. Stratum corneum
B. Stratum basale
C. Stratum lucidum
D. Stratum germinatum
Answer: A
44. Groove sign of greenbalt is seen in ?
A. LGV
B. Donovanosis
C. Chancroid
D. Genital Herpes
Answer: A
45. Mutation in which collagen is present in epidermolysis bullosa ?
A. II
B. IV
C. V
D. VII
Answer: D
46. Onychomycosis is most commonly caused by ?
A. A. Trichophyton rubrum
B. Trichophyton mentagrophytes
C. Epidermatophyton floccosum
D. A. Candida
Answer: A
47. RAST test is used in diagnosis of
A. Allergic dermatitis
B. Seborrhoeicdematitis
C. Mycosis fungoides
D. Squamous cell carcinoma
Answer: A
48. Characteristic of chronic eczema ?
A. Erythema
B. Induration
C. Lichenification
D. Edema
Answer: C
49. Sex worker with discharging ulcer, gram negative diplococci & growth on modified Thayer martin media. Diagnosis ?
A. N. gonococci
B. Syphilis
C. LGV
D. Chaneroid
Answer: A
50. Difference in acne rosacea & acne vulgarisa) Pustule
B. Erythema
C. Papule
D. Absence of comedone
Answer: D
51. Frequency of woods lamp is ?
A. 365 nm
B. 400 nm
C. 320 nm
D. 200 nm
Answer: A
52. Lovibond profile sign is seen in ?
A. Koilonychia
B. Platynochia
C. Clubbing
D. Onycholysis
Answer: C
53. Which hormone is responsible for acne ?
A. Estrogen
B. Thyroid
C. Testosterone
D. Gonadotropins
Answer: C
54. Hanifin & Rajke is the diagnostic criteria for
A. Atopic dermatitis
B. Contact dermatitis
C. Urticaria
D. Erythroderma
Answer: A
55. Treatment of choice of scabies in pregnancy ?
A. Ivermectin
B. Garna-benzen hexachloride
C. Permethrin
D. Garna-benzen hexachloride
Answer: Cact allergic
56. Most common metal in contdermatitis is?
A. Gold
B. Silver
C. Aluminium
D. Nickel
Answer: D
57. Skin scrapping & KOH mounting is done for ?
A. Leprosy
B. Varicella
C. Fungus
D. HSV
Answer: C
58. Lines of Blaschko’s are related to ?
A. Keratinocytes
B. Blood vessels
C. Nerves
D. Bones
Answer: A
59. Treatment of graunolma inguinale is ?
A. Tetracycline
B. Azithromycin
C. Clarithromycin
D. Streptomycin
Answer: B
60. The following drug is effective in treatment of ptyriasis versicolor ?
A. Ketoconazole
B. Metronidazole
C. Griseofulvin
D. Chloroquine
Answer: A
61. Keivms skin test is used for diagnosis of
A. Sarcoidosis
B. Wegeners granulomatosis
C. Graves disease
D. None
Answer: A
62. Drug of choice for treating chylmydia with gonorrhea is ?
A. Ciprofloxacin
B. Norfloxac in
C. Nalidixic acid
D. Doxycycline
Answer: D
63. Single dose treatment for gonorrhea ?
A. Azithromycin
B. Tetracyline
C. Ceftriaxone
D. Erythromycin
Answer: C
64. Erythroderma % of skin involved is ?
A. >90%
B. <30%
C. 30-60%
D. 60-70%
Answer: A
65. Drug causing fixed drug eruption ?
A. Sulfonamide
B. Erythromycin
C. Aminoglycoside
D. None
Answer: A
66. Pathergy test is used for ?
A. Reither’s syndrome
B. Bechet’s syndrome
C. Lichen planus
D. Atopic dermatitis
Answer: B
67. Tzank smear in varicella-zoster shows ?
A. Acantholysis
B. Spongiosis
C. Multinucleated Giant cell
D. Necrotic cell
Answer: C
68. Dead layer of epidermis ?
A. Stratum basale
B. Straum spinosum
C. Stratum corneum
D. Stratum granulosum
Answer: C
69. Which of the following cause noncicatracial alopecia ?
A. Tenia capitis
B. SLE
C. Alopecia areata
D. All of the above
Answer: D
70. Nail pitting is caused by all except ?
A. Lichen planus
B. Hyperthyroidism
C. Fungal infection
D. Pityriasis Rosacea
Answer: D
71. A pregnant lady comes with itchy hand lesions as shown. Her husband also gets it. The best treatment that can be given is ?
A. Permathrin
B. Ivermectin
C. GBH
D. Benzyl benzoate
Answer: A
72. Spongiosis involves ?
A. Stratum basal
B. Stratum carneum
C. Stratum granulosum
D. Stratum spinosum
Answer: D
73. Rain drop pigmentation is caused by ?
A. Clofazimine
B. Dapsone
C. Minocycline
D. Arsenic
Answer: D
74. man with pain in defecation, no gastrointestinal symptoms, clustered ulcers extending into anal canal. Diagnosis
a) CM V
B. Gonorrhea
C. Herpes genitalis
D. HIV
Answer: C
75. Acanthosis nigricans is seen in ?
A. Diabetes
B. GIT cancer
C. Hypothyroidism
D. All of the above
Answer: D
76. Circle of Hebra is involved in ?
A. Pediculosis corpora
B. Pityriasis versicolar
C. Scabies
D. Leprosy
Answer: C
77. Drug causing exanthema ?
A. Atropine
B. Phenytoin
C. Sulfonamide
D. All of the above
Answer: D
78. A 15cm hyperpigmented macule on an adolosent male undergoes changes such as coarceness, growth of hair & acne. Diagnosis is ?
A. Melanocytic nevus
B. Becker nevus
C. Sebaceous nevus
D. Sebaceous nevus
Answer: B
79. All are seen in Behchets syndrome except
A. Genital ulcers
B. Genital ulcers
C. Oral ulcers
D. Pyoderma gangrenosum
Answer: D
80. Ulcer necrotic nodule is seen in ?
A. Lucio leprosy
B. Lucio leprosy
C. Indeterminate leprosy
D. Histoid leprosy
Answer: A
81. Scalp and face are involved in ?
A. Adult scabies
B. Nodular scabies
C. Infantile scabies
D. None
Answer: C
82. Nerves are not involved in ?
A. Tuberculoid leprosy
B. Lepromatous leprosy
C. Indeterminate leprosy
D. Borderline tuberculoid leprosy
Answer: C
83. Grattage test is used for
a) Tinea capitis
B. Lichen planus
C. Pemphigus vulgaris
D. Psoriasis
Answer: D
84. Treatment of choice for lichen planus ?
A. Topical corticosteroids
B. Systemic corticosteroids
C. Antihistaminic
D. Acitretin
Answer: A
85. Keratodermic sandles is a feature of ?
A. Pityriasis rosacea
B. Lichen planus
C. Psoriasis
D. Pityriasis rubra pilaris
Answer: D
86. Schamberg’s purpura are seen on ?
A. Face
B. Feet
C. Chest
D. Arms
Answer: B
87. Nikolsky’s sign is seen in ?
A. Pemphigus
B. Herpes zoster
C. Bullous impetigo
D. All of the above
Answer: D
88. Erythema multiforme is most commonly caused by?
A. Herpes simplex
B. Idiopathic
C. TB
D. Drugs
Answer: B
89. Eyebrows don’t grow beyond certain length as they have a short ?
A. Anagen phase
B. Telogen phase
C. Telogen phase
D. Exogen phase
Answer: A
90. Not a cutaneous porphyria ?
A. Erythropoeitic porphyria
B. Hereditary coproporphyria
C. Congenital erythropoeitic porphyria
D. Sideroblastic anemia
Answer: B
91. Potato nose is seen in ?
A. Acne vulgaris
B. Rhinosporoidosis
C. Acne rosacea
D. Lupus vulgaris
Answer: C
92. Bullous impetigo is caused by ?
A. Streptococcus
B. Staphylococcus
C. Staphylococcus
D. Y. Pestis
Answer: B
93. Match stick test is positive in ?
A. Rhinophyma
B. Rhinosporiodosis
C. Lupus vulgaris
D. P. versicolor
Answer: C
94. On back, big black patch diagnosis is ?
A. Seborrheic melanosis
B. Becker nevus
C. Lichen planus pigmentosus
D. Pityriasis versicolor
Answer: B
95. Which of the following ultra-violet radiation cause most skin disorder ?
A. UV-A
B. UV-B
C. UV-C
D. None
Answer: B
96. Dermatophyes affect ?
A. Keratin
B. Dermis of skin
C. Stratum basal
D. Stratum basal
Answer: A
97. Treatment of dermatitis herpetiformis ?
A. Gluten free diet
B. Dapsone
C. Sulfonamide
D. All of the above
Answer: A
98. Brown macular pigmentation in malar area in a pregnant female is due to ?
A. Acne rosacea
B. Cholasma
C. Acanthosis nigricans
D. Urticaric pigmentosa
Answer: B
99. 15 mm/cm hyperpigmented lesion on shoulder enlarging and hair over it ?
A. Melanocytic nevus
B. Becker nevus
C. Sebaceous nevus
D. Comedo nevus
Answer: B
100. All are true about skin except:
A. Both dermis & ectoderm are derived from ectoderm
B. Skin accounts for total of 15% of body weight
C. Most of the cells in skin are keratinocytes derived from ectoderm
D. Dermis is made up of type1 and type 3 collagen in 3:2 ratio
Answer: A
101. Identify the condition in the image?
A. Leukoderma
B. Piebaldism
C. Vitiligo
D. DLE
Answer: A
102. Acantholysis is /are not seen in :
A. Lichen planus
B. Bullous pemphigoid
C. Dermatitis herpetiformis
D. Hailey-Hailey disease
E. Pemphigus vulgaris
Answer: A:B:C
103. Which of the following epidermal layer is dead layer?
A. Stratum basale
B. Stratum spinosum
C. Stratum corneum
D. Stratum granulosum
Answer: C
104. Langerhans cell are seen in which layer of skin?
A. Stratum basal
B. Stratum carneum
C. Stratum granulosum
D. Stratum spinosum
Answer: D
105. Increase in the thickness of the prickle cell layer of the epidermis is called?
A. Spongiosis
B. Acanthosis
C. Hypergranulosis
D. Hyperkeratosis
Answer: B
106. Substance common in skin and hair is?
A. Keratin
B. Laminin
C. Nectin
D. Vimentin
Answer: A
107. Which of the following is a melanising agent?
A. Methoxsalen
B. Dapsone
C. Minocycline
D. Kojic acid
Answer: A
108. Fordyce spots involve?
A. Penis
B. Tongue
C. Fingers
D. Nails
Answer: A
109. Most common etiology of erythema multiforme is?
A. Idiopathic
B. Drugs
C. HSV
D. TB
Answer: A
110. Hypopigmented macules are found in?
A. Addison’s disease
B. Porphyria
C. Cutaneous mastocytosis
D. Tuberous sclerosis
Answer: D
111. Which of the following disease is closely related to enteropathy?
A. Linear Ig A disease
B. Pemphigus foliaceous
C. Dermatitis herpetiformis
D. Erythema multiforme
Answer: C
112. Residual Hypopigmentation following a drug reaction, is best known as?
A. Vitiligo
B. Chemical leukoderma
C. Post inflammatory hypomelanosis
D. Piebaldism
Answer: C
113. Most common pattern of onychomycosis is?
A. Distal and lateral subungual
B. Proximal subungual
C. White superficial
D. Total dystrophic
Answer: A
114. Which of the following is not a feature of dermatomyositis?
A. ‘V’ sign
B. Holster sign
C. Pokiloderma
D. Groove sign
Answer: D
115. Not a feature of candidal intertrigo is?
A. Obesity is a risk factor
B. C. albicans is the most common causative species
C. Central scaling
D. Satellite lesions
Answer: C
116. Nevus simplex commonly presents at ?
A. Face
B. Trunk
C. Legs
D. Hand
Answer: A
117. Scaling is not feature of which of the following?
A. Tinea
B. Lichen planus
C. Herpes zoster
D. Reiter’s disease
Answer: C
118. A 40 years old male patient presents with multiple erythematous annular lesions with peripheral scales arranged predominantly on trunk. Treatment of choice is?
A. Topical steroids
B. Systemic steroids
C. Systemic Azathioprine
D. Topical antifungal
Answer: A
119. Woronoff’s ring is a feature of?
A. Psoriasis
B. Lichen planus
C. Pityriasis rosea
D. Pemphigus
Answer: A
120. True about erythema toxicum is?
A. Common in pre-term baby
B. Lesions contain many lymphocytes
C. Can be life threatening condition
D. Occurs mainly in neonatal period
Answer: D
121. Most important factor in causation of Ingrown toe nail is?
A. Fungal infection
B. Ill fitting shoes
C. Genetic predisposition
D. Nutritional deficiency
Answer: B
122. Which of the following is true about xeroderma pigmentosa?
A. Autosomal dominant
B. Good long term prognosis
C. Purine dimmers
D. DNA repair defect
Answer: D
123. Which of the following is not a feature of lichen planus?
A. Pterygium
B. Spontaneous healing
C. Scarring alopecia
D. Not premalignant
Answer: D
124. Most common metal responsible for contact dermatitis is ?
A. Gold
B. Silver
C. Nickel
D. Mercury
Answer: C
125. Which of the following is not true for scabies?
A. Wrist is common site in children
B. Burrows are intradermal lesions
C. Papules and pustules are due to hypersensitivity to mite
D. Itching generalized
Answer: B
126. Treatment of choice for oral candidiasis is?
A. Terbinafin
B. Nystatin
C. Griesofulvin
D. Selenium sulphide
Answer: B
127. Scabies is caused by?
A. Mite
B. Tic
C. Virus
D. Fungus
Answer: A
128. Volcano sign is seen in?
A. Leprosy
B. Leishmaniasis
C. Lupus vulgaris
D. DLE
Answer: B
129. Selenium sulphide is used in the treatment of?
A. Scabies
B. T. versicolor
C. T. cruris
D. Cutaneous leishmaniasis
Answer: B
130. First generation topical retinoid is?
A. Retinoic acid
B. Adapalene
C. Tazarotene
D. Acitretin
Answer: A
131. Most common type of cutaneous mastocytosis is?
A. Solitary mastocytoma
B. Urticaria pigmentosa
C. Telangiectasia macularis eruptiva perstans
D. Diffuse erythrodermic
Answer: B
132. Treatment for impetigo includes all except?
A. Topical mupirocin
B. Systemic erythromycin
C. Topical gentamycin
D. Systemic cephalosporins
Answer: C
133. False about Langer’s lines is?
A. Remain constant throughout life time of a person
B. Correspond to the collagen fibers in dermis
C. Incision along these lines produces better scar
D. Skin along these lines is least flexible
Answer: A
134. Jock itch is caused by?
A. Epidermophyton floccosum
B. Candida albicans
C. Trichophyton tonsurans
D. Malassezia furfur
Answer: A
.
135. Resorcinol is used in the treatment of?
A. Lichen planus
B. Acne
C. Vitiligo
D. Scabies
Answer: B
136. Multiple psoriatic lesions on hands. Treatment of choice is?
A. NBUVB
B. Systemic methotrexate
C. Topical steroids and salicylic acid
D. Systemic steroids
Answer: C
137. Hertoghe’s sign is seen in?
A. Atopic dermatitis
B. Cutaneous TB
C. Lichen planus
D. Psoriasis
Answer: A
138. Treatment of choice for erythrodermic psoriasis is?
A. Prednisolone
B. Hydroxyurea
C. Acitretin
D. Ciclosporin
Answer: C
139. Preferred concentration of minoxidil for female androgenetic alopecia is?
A. 2%
B. 5%
C. 8%
D. 10%
Answer: A
140. Normal epidermal turnover time is?
A. 1 week
B. 2 weeks
C. 3 weeks
D. 4 weeks
Answer: C
SKIN Objective Questions with Answers
141. Alopecia universalis is?
A. Loss of all the scalp hair
B. Loss of all body hair
C. Loss hair at the scalp margin
D. Male pattern hair loss
Answer: B
142. Treatment of choice for scabies in an infant < 6 months is?
A. BHC
B. Ivermactin
C. Permathrin
D. Crotomiton
Answer: D
143. A known case of diabetes develops annular orange skin lesions, which disappear after biopsy. This phenomenon is known as?
A. Koebner’s phenomenon
B. Reverse Koebner’s phenomenon
C. Asboe Henson sign
D. Isotopic phenomenon
Answer: B
144. Oral treatment of choice for scabies is?
A. Albendazole
B. Itraconazole
C. Sulphur
D. Ivermactin
Answer: D
145. Pityriasis rosea clears with in?
A. 1-2 weeks
B. 2-4 weeks
C. 4-8 weeks
D. 6-12 weeks
Answer: B
146. Periungual desquamation, which is a characteristic feature of Kawasaki syndrome, occurs at ?
A. 1st-2nd week
B. 2nd-3rd week
C. 3rd-4th week
D. 4th_5th week
Answer: B
147. True about Keratinocyte is ?
A. Ectoderm derived cell
B. Present only in basal layer
C. Mature in basal layer
D. Differentiate in basal layer
Answer: A
148. Odland bodies are seen in which layer of epidermis?
A. Basal cell layer
B. Prickle cell layer
C. Stratum granulosum
D. Stratum corneum
Answer: C
149. Which of the following drug can lead to pemphigus?
A. Penicillamine
B. Isoniazid
C. Carbamazepine
D. Furosemide
Answer: A
150. In which of the following phototherapy is useful in treatment ?
A. Psoriasis
B. Tinea corporis
C. Pemphigus
D. PMLE
Answer: A
151. All are true about actinic lichen planus except ?
A. Associated with severe pruritus
B. Autoimmune etiology
C. Voilaceous brown papules
D. Usually affects exposed areas of body
Answer: A
152. Acanthosis nigricans is characterized by all of the following except ?
A. Common in obese people
B. Associated with thick skin with hyperpigmentaion
C. Histologically there is hypermelanosis
D. May be a sign of internal malignancy
Answer: C
153. Which of the following is characterized by a solitary painless ulcer on genitalia?
A. Herpes
B. Soft chancre [chancroid]
C. Hard chancre
D. Traumatic ulcer
Answer: C
154. Epidermal nevus follows ?
A. Blaschko’s lines
B. Langer’s lines
C. Vasculature
D. Lymphatics
Answer: A
155. Which of the following organism has a role to play in Seborrhic dermatitis ?
A. Pityrosporum ovale
B. Canida albicans
C. Propionibacterium
D. None of the above
Answer: A
156. Pruritus is a feature of which of the following ?
A. Pemphigus foliaceous
B. Pemphigus vulgaris
C. Bullous Pemphigoid
D. All of the above
Answer: C
157. Goekarman regimen used in for treatment of psoriasis is?
A. UVB plus coal tar
B. UVB plus anthralin
C. Coal tar plus anthralin
D. UVB plus methotrexate
Answer: A
158. True regarding Bowen’s disease is ?
A. In situ BCC
B. More common in dark skinned people
C. HSV infection plays a role
D. Chronic sun damage plays a role
Answer: D
159. Among various types of psoriatic arthrirtis, which variety is most common ?
A. Classic
B. Oligoarticular
C. Rheumatoid
D. Spondylitis
Answer: B
160.All of the followings are part of the treatment of scabies except?
A. Topical Permathrin
B. Oral ivermactin
C. Oral antihistamines
D. Long term oral steroids
Answer: D
161. Drug of choice for bubos in a pregnant female is ?
A. Tetracycline
B. Doxycycline
C. Ceftriaxone
D. Erythromycin
Answer: D
162. Which ‘P’ is not a feature of lichen planus ?
A. Polygonal
B. Polyhedral
C. Pruritus
D. Plane
Answer: B
163. In lichen planus all the following sites are affected except ?
A. Flexor aspect of upper extrimities
B. Oral mucosa
C. Nails
D. Extensor aspect of upper extrimities
Answer: D
164. Bull’s eye lesions are found in ?
A. Erythema nodosum
B. Erythema gangrenosum
C. Erythema multiforme
D. Erythroderma
Answer: C
165. Not a hemorrhagic lesion ?
A. Petechiae
B. Echymosis
C. Plaque
D. None of the above
Answer: C
166. Maculae cerulea is seen in ?
A. Pediculosis hominis corporis
B. Pediculosis capitis
C. Scabies
D. Lupus erythematosus
Answer: A
167. Most common site for atopic dermatitis
A. Scalp
B. Trunk
C. Popliteal fossa
D. Knees
Answer: C
168. Incontinentia pigmenti involves all exept ?
A. Skin
B. Bones
C. Teeth
D. Heart
Answer: D
169. Not true about Skin tag ?
A. Associated with seborrhoeic keratosis
B. Pedunculated
C. Most common site is neck and axilla
D. Premalignant
Answer: D
170. Spider telengectacia false is ?
A. More common in males
B. Can be caused by trauma
C. Light therapy for treatment
D. May be associated with liver disease
Answer: A
171. Which of the following is untrue regarding piebaldism?
A. autosomal dominant condition
B. amelanotic skin associated with a white forelock
C. Islands of normal or hypermelanotic skin
D. Usually improves with age
Answer: D
172. Which of the following is not a NEVUS of melanocyte?
A. Mongolian spot
B. Nevus of Ito
C. Nevus of ota
D. Becker nevus
Answer: D
173. Ichy purple papule followed by hyper pigmentation on resolution, is seen in?
A. Addison’s disease
B. DM
C. Hypothyroidism
D. Lichen planus
Answer: D
174. Loss of Intercellular cohesion between keratinocytes is called as ?
A. Acanthosis
B. Acantholysis
C. Keratinolysis
D. Spongiosis
Answer: B
175. Tzank cell is ?
A. Keratinocyte
B. Fibrobalst
C. Neutrophil
D. Lymphocyte
Answer: A
176. True about lepromatous leprosy ?
A. Only 3 cutaneous lesions
B. Lepromin test highly positive
C. Thickened nerve roots
D. ENL in > 50% cases
Answer: C
177. Dermatophytosis is not ?
A. Scaly
B. Itchy
C. Superficial
D. Subdermal
Answer: D
178. Oculoorogenital ulcers are a feature of ?
A. Behcet disease
B. lichen planus
C. SLE
D. Psoriasis
Answer: A
179. Maximum cumulative dose of isotretinoin shouldn’t exceed for acne treatment ?
A. 30-60 mg/kg
B. 60-90 mg/kg
C. 90-120 mg/kg
D. 120-150 mg/kg
Answer: D
180. Exanthema subitum is caused by ?
A. HHV
B. HPV
C. HIV
D. HCV
Answer: A
181. Cutis marmorata occurs due to exposure to –
A. Cold temperature
B. Dust
C. Hot temperature
D. Humidity
Answer: A
182. What constitutes malpighian layer?
A. Corneum lucidum
B. Corneum spinosum
C. Spinosum and basale
D. Basale granulosum
Answer: C
183. A Child is born, covered with a thick membranous coat, what could be the possible diagnosis?
A. Lamellar ichthyosis
B. X-linked ichthyosis
C. Ichthyosis Vulgaris
D. Ichthyosis acquista
Answer: A
184. Lines of Blaschko represent:
A. Lines along lymphatics
B. Lines along blood vessels
C. Lines along nerves
D. Lines of development
Answer: D
185. All are features of atopic dermatitis, except:
A. Dennie -Morgan fold
B. Hertoghe’s sign
C. Darier’s Sign
D. Hyperlinearity of palms
Answer: C
186. All of the following are true about incontinentia pigmenti, except:
A. Ocular involvement is seen in almost 100% cases and is typically unilateral
B. Avascularity of peripheral retina
C. Primary skin abnormality
D. X-linked dominant
Answer: A
187. Pemphigus vulgaris is characterized by all, except:
A. Positive Nikolsky’s sign
B. Oral erosions
C. Subepidermal bulla
D. Tzanck smear showing acantholytic cells
Answer: C
188. Which of the following is the agent of choice for cryosurgery?
A. Nitrous oxide
B. CO2 snow
C. Liquid nitrogen spray
D. Freons
Answer: C
189. Treatment of nodulocystic acne is
A. Erythromycin
B. Tertacycline
C. Isoretinonine (Retinoic acid)
D. Steroids
Answer: C
190. Anagen phase of the hair indicates:
A. The phase of activity and growth
B. The phase of transition
C. The phase of resting
D. The phase of degeneration
Answer: A
191.the stratum corneum is composed of ?
A. melanin
B. granules
C. keratin cells
D. squamous cells
Answer: C
192.which layer is the top, or uppermost, layer of the epidermis?
A. dermis
B. stratum corneum
C. stratum mucosum
D. stratum granulosum
Answer: B
193. Fox Fordyce Disease effects:
A. Sebaceous glands
B. Eccrine Glands
C. Apocrine glands
D. Any gland
Answer: C
194. A melanocytic naevus surrounded by a depigmented halo is called:
A. Sutton’s nevus
B. Meyerson’s naevus
C. Cockade naevus
D. Nevus anaemicus
Answer: A
195. Which of the following is the most common form of malignant melanoma?
A. Nodular
B. Superficial spreading
C. Acral lentiginous
D. Mucosal
Answer: B
196.where are the blood vessels found that supply the skin?
A. dermis
B. epidermis
C. stratum lucidum
D. stratum corneum
Answer: A
197. sudoriferous glands, sebaceous glands sensory nerve endings, blood vessels, arrector pili muscles and a major portion of each hair follicle are found in the ?
A. dermis
B. epidermis
C. stratum corneum
D. startum spinosum
Answer: A
198. what part of the skin is often referred to as “true skin”
A. dermis
B. epidermis
C. stratum corneum
D. stratum spinosum
Answer: A
199. which layer of the skin produces collgen protein and elastin fibers to help give the skin its elasicity and pliability?
A. dermis
B. epidermis
C. stratum lucidum
D. stratum graninativum
Answer: A
200. the deterioration of collagen and elastiin fibers during fibers during the aging process causes?
A. rosacea
B. freckles
C. macules
D. wrinkles
Answer: D
201.the sudoriferous (sweat) glands are referred to as:
A. nervous system
B. muscular system
C. endocrine system
D. circulatory system
Answer: A
202.sudoriferous and sebaceous glands are referred to as ?
A. pores
B. follicles
C. duct glands
D. ductless glands
Answer: C
203.control and regilation of body temperature by the sudoriferous glands help maintan the body temperture at?
A. 78.0 f or 29.4 c
B. 94.0 f or 87.9 c
C. 88.6 f or 37 c
D. 98.6 f or 37 c
Answer: D
204.the greatest concentration of sudorferous glands is found on the?
A. arms
B. eyelids
C. midsection of the body
D. palms, soles,scalp and forehead and underarms
Answer: D
205.the sebaceous gland produces:
A. melanin
B. dandruff
C. sebum (oil.
D. perspiration
Answer: C
206. on what area of the body would you not find any sebaceous glands?
A. the face
B. in the groin area
C. on the arms and legs
D. on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet
Answer: D
207.what is the function of sebum?
A. carry melanin
B. produce sweat
C. give skin elasticity
D. keep skin from drying and chapping
Answer: D
208.the papillary canal take oil (sebum) to the?
A. nerve
B. keratin
C. blood vessels
D. surface of the skin
Answer: D
209.where is the layer of skin called the subcutaneous layer located ?
A. above the cuticle
B. below the dermis
C. above the epidermis
D. below the adipose tissue
Answer: B
210.the subcutaneous tissue of skin is made up of mostly?
A. keratin
B. muscle
C. melanin
D. fatty cells
Answer: D
211.what layer of the skin contains large blood vessels that transport nouishment to skin and nerve ?
A. epidermis
B. melanin layer
C. spinum spinosum
D. subcutaneous layer
Answer: D
212.what factor would cause a reaction in sensory nerve fibers?
A. fear
B. light
C. sound
D. cold temperatures
Answer: D
213.what tans the skin to help protect it from harmful ultraviolet rays?
A. sebum
B. melanin
C. the acid mantle
D. the subcutaneous layer
Answer: B
214.light skin and dark skin differ in the ?
A. number of melanocytes the contain
B. rate and amount of melanin produced
C. number of nerve endings the contain
D. number of epidermal cells they contain
Answer: B
215.almost 90% of the skin’s wrinkles are caused by ?
A. exposure to the sun
B. exposure to pollutants
C. excessive use of astringents
D. excessive exposure to fluorescent lights
Answer: A
216.on the human body, the thinnest skin is located on the ?
A. chin
B. eyelids
C. soles of the feet
D. skull just behind the ears
Answer: B
217.healthy skin’s pH level of 4.5 to 5.5 is?
A. highly acidic
B. acid-balanced
C. highly alkaline
D. slightly alkaline
Answer: B
218.how should a salon profession react if the client has a skin disease?
A. prescribe proper treatment
B. suggest home remedies to client
C. perform the service while wearing gloves
D. refer client to a physician or dermatologist
Answer: D
219.chronic is the term used to identify condition that are ?
A. visible
B. brief and severe
C. frequent and habitual
D. influenced by weather
Answer: C
220.the term used to identify conditions that are brief and severe is ?
A. acute
B. chronic
C. objective
D. subjective
Answer: A
221.a disease that spreads by personal contact is known as?
A. systemic
B. congenital
C. contagious
D. occupational
Answer: C
222.a disease influenced by weather is referred to as?
A. serial
B. rational
C. seasonal
D. inflammable
Answer: C
223.what is the technical name for the study of the cause of diseases?
A. etiology
B. anatomy
C. pathology
D. dermatology
Answer: A
224.what is the technical term for the study of deseases?
A. eitology
B. anatomy
C. pathology
D. dermatology
Answer: C
225.indicating a medical opinion of a future condition of illness is known as a?
A. analysis
B. diagnosis
C. prognosis
D. recognition
Ams: c
226.an alleegic reaction to cosmetics or chemicals which salon professionals may be susceptible to is called?
A. papules
B. chloasma
C. lenigines
D. sermatitis venenata
Answer: D
227.an example of a subjective symptom would be?
A. itching
B. swelling
C. redness
D. discharge
Answer: A
228.abnormal changes in the structure of organs or tissues are called primary and secondary?
A. wheal
B. fissure
C. lesions
D. infection
Answer: C
229.a freckle is an example of which type of primary skin lesion?
A. lentigo
B. papule
C. macule
D. leukoderma
Answer: C
230.a papule is an example of a ?
A. tertiary lesion
B. primary skin lesion
C. subjective symptom
D. secondary skin lesion
Answer: B
231.vesicles can be produced by which of the following conditions?
A. callus
B. verrucas
C. poison ivy
D. dry, scaly skin
Answer: C
232.herpes simplex is the technical term for?
A. acne
B. eczema
C. psoriasis
D. fever blisters
Answer: D
233.a solid mass in the skin that could be soft or hard, fixed or freely movable and may be elevated or deep is called a ?
A. crust
B. callus
C. tumor
D. wheal
Answer: C
234.a cyst is defined by which of the following description?
A. oozing sore
B. wheal lesions
C. crack in the skin
D. abnormal membranous sac
Answer: D
235.a secondary lesion appearing as round, dry patches of skin covered with rough, silvert scales is called?
A. acne
B. eczema
C. psoriasis
D. herpes simplex
Answer: C
236.which of the following skin lesions often occurs when skin loses its flesibility due to exposure to wind, cold, water, etc and cracks in the skin appear?
A. stain
B. tumor
C. fissure
D. papule
Answer: C
237.the lesion found following the healing of an injury is called a(n.?
A. vitiligo
B. fissure
C. scar
D. excoriation
Answer: C
238.which of the following terms is another name for a keratoma?
A. a wart
B. a callus
C. a tumor
D. a birthmark
Answer: B
239.what may happen to the skin if an area is subject to pressure or friction over a long period of time?
A. it may wear thin
B. it may become shiny
C. it may scale and flake
D. it may become callused
Answer: D
240.verruca is a name given to a variety of?
A. warts
B. ulcers
C. fissures
D. skin tags
Answer: A
241.melanotic sarcoma is a skin cancer that begins with?
A. a mole
B. an ulcer
C. lentigines
D. miliaria rubra
Answer: A
242.what is the technical name for liver spots?
A. rubra
B. crustacea
C. chloasma
D. leukoderma
Answer: C
243.what is another name for a stain in the skin caused by the dilation of the small blood vessels in the skin, also known as a birthmark?
A. scar
B. callus
C. nevus
D. verruca
Answer: C
244.comedone is the technical name for?
A. nevus
B. macule
C. blackhead
D. whitehead
Answer: C
245.what is the techical term for a decrease in activity of melanocytes?
A. acne
B. verruca
C. leukoderma
D. melanoderma
Answer: C
246.accumulations of hardened sebum beneath the skin are called whiteheads or:
A. acne
B. milia
C. rosacea
D. comedones
Answer: B
247.acne most often occurs on the ?
A. legs, hips, and arms
B. face, back and chest
C. fingers, toes and soles
D. ankles, knees and elbow
Answer: B
248.acne can be found in two stages, acne simplex and:
A. rosacea
B. asteatosis
C. acne vulagarsis
D. deep-seated acne
Answer: C
249.what is the professional action to take when a client with rosacea requests a facial service with you?
A. refer clients to another salon
B. avoid the issue of rosacea
C. proceed with the service but wear protective gloves
D. proceed with the service with approval of the client’s physician
Answer: D
250.what is a condition called that is characterized by dry, scaly skin caused by a decreased production of sebum?
A. rosacea
B. steatoma
C. asteatosis
D. seborrhea
Answer: C
251.which disorder is caused by excessive secretion of the sebaceous glands?
A. millia
B. asteatosis
C. seborrhea
D. bromidrosis
Answer: C
252.where does a steatoma most often appear?
A. on the arms, legs and chest
B. on the face, feet and hands
C. on the fingers, feet and toes
D. on the scalp, neck and back
Answer: D
253.what is the definition of bromidrosis?
A. excessive sebum
B. the lack of sebum
C. the lack of perspiration
D. foul-smelling perspiration
Answer: D
254.the lack of perspiration caused by fever or disease is called?
A. anhidrosis
B. osmidrosis
C. bromidrosis
D. hyperhidrosis
Answer: A
255.what is the disorder called that is an overproduction of perspiration caused by excessive heat or general body weakness?
A. osmidrosis
B. anhidrosis
C. bromidrosis
D. hyperhidosis
Answer: D
256.which of the following terms does NOT describe a guideline that can indicate skin cancer?
A. color
B. border
C. texture
D. asymmetry
Answer: C
257.products that work tofurther cleanse the skin and return it to its normal pH include?
A. oils
B. massage creams
C. manual exfoliants
D. astringents and tonic lotions
Answer: D
258.a term that is used to describe moisturizing is ?
A. oiling
B. toning
C. hydrating
D. cleansing
Answer: C
259.applying pressure to motor points will have which of the following effects?
A. inflame and irrtate muscles
B. increase secretion
C. decrease production
D. soothe and stimulate nerves and muscles
Answer: D
260.effleurage is a massage movement that involves a:
A. circular movement with no gliding
B. light tapping or slapping movement
C. light, gentle stroking or circular movement
D. light or heavy kneading and rolling of muscles
Answer: C
261.the gentle massage movement that often begins and ends a massage treatment is ?
A. vibration
B. effleurage
C. petrissage
D. tapotement
Answer: B
262.the massage manipulation that consists of heavy kneading and rolling of the muscles is called:
A. friction
B. vibration
C. petrissage
D. tapotement
Answer: C
263.which massage manipulation deeply stimules the muscles, nerves and skin glands?
A. friction
B. vibration
C. petrissage
D. tapotement
Answer: C
264.the massage movement that should not be used when the client needs soothing is?
A. gliding
B. stroking
C. effleurage
D. tapotement
Answer: D
![MCQs [2024]](https://engineeringinterviewquestions.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/Interview-Questions-2.png)