Throat Disorders Multiple Choive Questions
1. This disorder occurs in children 2 to 12 years of age and may occur in infants. There may be a history of maternal human papillomavirus: may be recurrent and progressive. Physical signs are faint cry. severe stridor, voice change or complete aphonia.
- Laryngeal papillomas
- Polyps
- Gastro esophageal reflux disease (GERD)
- Neoplasm
- Vocal cord paralysis
2. There is a history of psychiatric illness or psychological trauma. The symptoms are a breathy, low voice and larynx appears normal.
- Vocal cord paralysis
- Hypothyroidism
- Neoplasm
- Psychogenic hoarseness
- Polyps
3. Persons with diabetes and those taking broad spectrum antibiotics are more susceptible to candidacies.
- False
- True
4. Clear nasal discharge is common in allergic pharyngitis and may produce postnasal drip that causes a sore throat.
- True
- False
5. Nasal congestion that leads to mouth breathing produces laryngeal dryness. with resultant hoarseness in the morning.
- True
- False
6. The symptoms are poor oral hygiene. painful ulcers, foul breath and bleeding gums. Examination shows gray necrotic ulcers without vesicles on gingival margins and interdentally papilla..
- Group A streptococcal pharyngitis
- Fusospirochetal infection (Vincennes angina)
- Gonococci pharyngitis
- Herpanglna (coxsackievlrus)
- Viral pharyngitis
7. Hoarseness is one of the early symptoms of hypothyroidism.
- True
- False
8. External trauma to the throat is a common cause of hoarseness.
- True
- False
9. The symptoms are voice overuse, exposure to environmental irritants and recent URI. The physical findings show cervical lymphadenopathy and edema and redness of the vocal cords.
- Acute epiglottises
- Trauma
- Acute laryngeal edema
- Acute laryngitis
- Laryngotracheobronchltis (croup)
10. The symptoms are chronic cough; inspiratory or expiratory strider with exertion. Examination shows a breathy, weak, soft voice and abnormal movement of vocal cords.
- Gastro esophageal reflux disease (GERD)
- Hypothyroidism
- Polyps
- Neoplasm
- Vocal cord paralysis
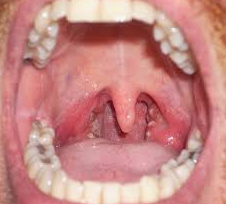
11. The symptoms are exposure to irritants; postnasal drip and allergic symptoms. Physical findings are sinus tenderness, pale or swollen pharynx, postnasal drainage visible, but no fever or lymphadenopathy.
- Her angina (coxsackievirus)
- Mononucleosis (Epstein-Barr virus)
- Group A streptococcal pharyngitis
- Inflammation
- Viral pharyngitis
12. A sore throat may be a symptom of systemic illness such as mononucleosis.
- True
- False
13. The symptoms are a history of recurrent tonsillitis: sore throat, difficulty in swallowing, respiratory tract symptoms, fever and malaise. Physical findings include orthopnea, dispend, symmetrical swelling, abscess and trismus.
- Candidacies
- Aphthous steatites
- Epiglottises
- Peritonsillar I retropharyngeal abscess
- Viral pharyngitis
14. The symptoms are scratchy, sore throat, malaise. myalgias, headache, chills, cough and rhinitis. Physical findings show erythematic. edema of throat and tender posterior cervical nodes.
- Group A streptococcal pharyngitis
- Her angina (coxsackievirus)
- Gonococcal pharyngitis
- Mononucleosis (Epstein-Barr virus)
- Vrai pharyngitis
15. The history may include smoking, airborne exposure, chronic alcohol use, history of chronic cough, hoarseness for more than 3 weeks. Physical examination shows tracheal deviation or pain with advanced tumor.
- Vocal cord paralysis
- Hypothyroidism
- Polyps
- Neoplasm
- Gastro esophageal reflux disease (GERD)
16. Epstein-Barr virus (mononucleosis) is highly contagious and spreads quickly among individuals.
- True
- False
17. There is a history of upper GI burning and cough especially at night: chronic use of alcohol. NSAIDS. or aspirin: history of ulcer disease, smoker, age less than 45 years and frequent throat clearing. Physical examination shows epigastric tenderness on palpation and vocal cord Inflammation or ulcers.
- Polyps
- Neoplasm
- Gastro esophageal reflux disease (GERD)
- Vocal cord paralysis
- Hypothyroidism
18. The throat pain produced by non-infectious causes tend to be less severe and may be described as scratchy” or “annoying’.
- False
- True
19. The symptoms are most common in young adults. There is a slow onset of malaise. low- grade fever, and mild sore throat. Physical findings show presence I absence of pharyngeal exudates, palatine petechiae. posterior cervical lymphadenopathy, and splenomegaly.
- Viral pharyngitis
- Group A streptococcal pharyngitis
- Her angina (coxsackievirus)
- Gonococci pharyngitis
- Mononucleosis (Epstein-Barr virus)
20. The patient has a history of trauma to mucosa; pain, fever and headache. Examination shows per oral lesions; lymphadenitis: vesicles on palate. pharynx and gingival.
- Viral pharyngitis
- Epiglottises
- Pathos steatites
- Candidacies
- Herpes simplex infection
21. Patients with GERD have a normal voice in the morning with progressive hoarseness throughout the day.
- True
- False
22. Hoarseness that is altered by a position change suggests a mobile lesion such as a pedunculated polyp.
- True
- False
23. Streptococcal pharyngitis or influenza in children older than 2 years of age is associated with complaints of headache, abdominal pain and vomiting.
- False
- True
24. There is a presence of systemic symptoms such as cold intolerance, weight gain, fatigue:
older than 65 years of age: postpartum women and a family history of thyroid disease. Physical examination shows a normal or enlarged thyroid gland, coarse hair, very dry skin and prolonged deep tendon reflex recovery.
- Polyps
- Gastro esophageal reflux disease (GERD)
- Hypothyroidism
- Neoplasm
- Vocal cord paralysis